vCenter High Availability (vCenter HA) protects vCenter Server Appliance against host and hardware failures. Also, the active-passive architecture of the vCenter HA solution will help to reduce downtime significantly when the patching of the vCenter Server Appliance required.
As we are aware that vCenter Server is an important part of vSphere Infrastructure for central management and using their advanced features to provide availability. Many of VMware infrastructure may face an issue like a crash of vCenter Server or vCenter Server is unable to start etc. And until the issue fixed you must manage all the ESXi hosts individually and it’s a difficult task if the number hosts are high.
VMware announced feature HA for the vCenter Server with vSphere 6.5 version, and the High Availability feature is available only with VCSA not with windows based vCenter Server. The vCenter Server Appliance has provided vCenter High Availability (HA) with vSphere 6.5 onwards. In the fully-functioning HTML5 release of vCenter 6.7 Update 1 onwards the setup of vCenter HA was incredibly simplified.
vCenter Architecture Overview
A vCenter HA cluster consists of three VCSA instances, the first instance initially used as the Active node, is cloned twice to a Passive node and to a Witness node. And together these three nodes provide an active-passive failover solution.
Deploying each of the nodes on a different ESXi instance protects against hardware failure. Adding the three ESXi hosts to a DRS cluster can further protect your environment. When the vCenter HA configuration is complete, only the Active node has an active management interface (public IP). The three nodes communicate over a private network called the vCenter HA network that is set up as part of the configuration. The Active node is continuously replicating data to the Passive node.
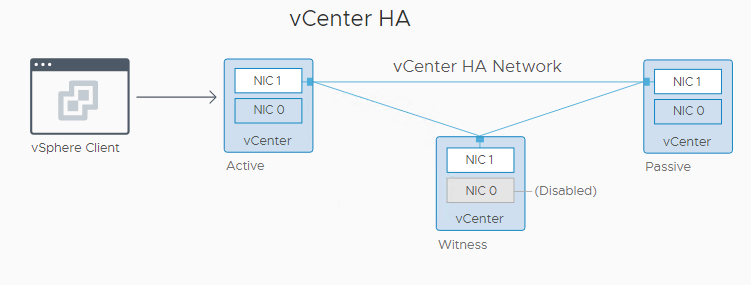
Active Node: Active node is the primary running vCenter Server Appliance instance that is currently running. The active node replicates data to the Passive node using the HA network to communicate with the Passive & Witness Node.
Passive Node: Passive Node is the clone of the Active node which created while configuring the HA for vCenter. It continuously receives updates from and synchronizes state with the Active node over the vCenter HA network. And the Passive Node takes over the role of the Active Node once the failover occurs.
Witness Node: Witness Node is a lightweight clone of the Active node and it serves as a quorum to protect against a split-brain situation.
vCenter HA Network: To configure vCenter HA there is HA network required. You can use the HA network by creating a new Port group or a new virtual switch with different subnet
vCenter HA Hardware and Software Requirements
Before you set up vCenter HA, ensure that you have sufficient memory, CPU, and datastore resources, and ensure that you are using versions of vCenter Server and ESXi that support vCenter HA.
Your environment must meet the following requirements

vCenter HA Deployment Options
vCenter HA environment can be deployed in two methods with an embedded Platform Services Controller or with an external Platform Services Controller. And the vCenter HA configuration can be performed in two modes, Automatic and Manual mode.
vCenter HA with an Embedded Platform Service Controller
To configure vCenter HA with an embedded Platform Service Controller is easy and straight forward, first you have to Deploy vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded Platform Services Controller and configure vCenter HA with help of separate HA network.
Once the vCenter HA deployment starts, First Cloning of the vCenter Server Appliance to a Passive and later to a witness node occurs. As part of the cloning process, Platform Services Controller and all its services are cloned as well.
Once the vCenter HA configuration is complete, vCenter HA performs replication to ensure that the Passive node is synchronized with the Active node. The Active node to Passive node replication includes Platform Services Controller data.

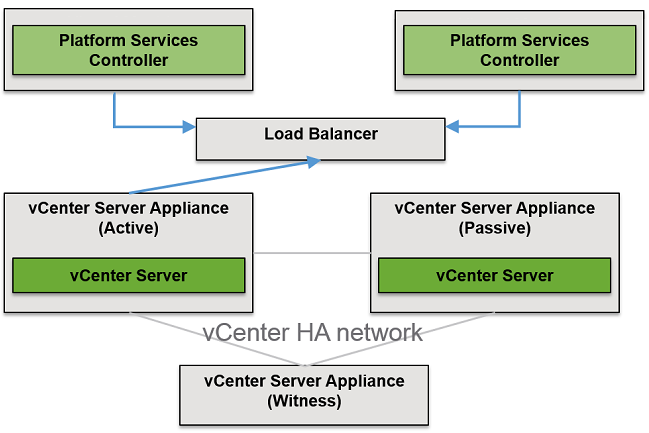
vCenter HA with an External Platform Service Controller
To configure vCenter HA with an external Platform Service Controller, you must set up an external load balancer to protect the Platform Services Controller. If one Platform Services Controller becomes unavailable, the load balancer directs the vCenter Server Appliance to a different Platform Services Controller.
To configure this, you must use at least two external Platform Service Controller instances and these instances replicate vCenter Single Sign-On information and other Platform Services Controller information. While deploying you must select the external Platform Services Controller and vCenter Server Appliance will point to a load balancer that provides high availability for Platform Services Controller.
And once the vCenter HA deployment starts first vCenter Server Appliance will clone a Passive node and later Witness node. Also, as part of the cloning process, the information about the external Platform Services Controller and the load balancer is cloned as well. Finally, the configuration is completed the vCenter Server Appliance is protected by vCenter HA.
If the Platform Services Controller instance becomes unavailable, the load balancer redirects requests for authentication or other services to the second Platform Services Controller instance.
Follow below supported VMware Knowledge Base articles for external Platform Services Controller deployment option
-
2147014: Configuring Netscaler Load Balancer for use with vSphere Platform Services Controller (PSC) 6.5
-
2147038 Configuring F5 BIG-IP Load Balancer for use with vSphere Platform Services Controller (PSC) 6.5
-
2147046 Configuring NSX Edge Load Balancer for use with vSphere Platform Services Controller (PSC) 6.5
Automatic Configuration
With automatic configuration mode, vCenter HA wizard automatically creates the Passive and Witness nodes. And you must meet one of the following requirements to perform automatic configuration.
- The vCenter Server Appliance that will become the Active node is managing its own ESXi host and its own virtual machine. This configuration is sometimes called a self-managed vCenter Server.
- The vCenter Server Appliance is managed by another vCenter Server. They both use an external Platform Services Controller, and both are running vSphere 6.5 or later.
Workflow for Automatic Configuration
- Deploy the first vCenter Server Appliance, which will become the Active node.
- Configure a network port group for vCenter HA traffic on all the ESXi hosts.
- Start the vCenter HA configuration and supplies the IP addresses, the target ESXi host or cluster, and the datastore for each clone.
- The deployment process will clone the Active node and creates a Passive node with precisely the same settings, including the same hostname.
- Once the Passive node created a system will clone the Active node again and creates a more light-weight Witness node.
- The system sets up the vCenter HA network on the three nodes to communicate with each other to exchange the information and replication
Manual Configuration
With the manual configuration mode, you must manually clone the Active node to create the Passive and Witness nodes. Also, to remove the vCenter HA configuration later, you have to manually delete the nodes that you created.
Workflow for Manual Configuration
- Deploy the first vCenter Server Appliance and configure the second network (port group) for vCenter HA traffic on each ESXi host.
- The user must add a second network adapter (NIC) to the Active node if the credentials of the Active management vCenter Server are unknown.
- Start the vCenter HA configuration by selecting the checkbox to manually configure and supplies IP address and subnet information for the Passive and Witness nodes. Optionally, the user can override the failover management IP addresses.
- The user logs in to the Management vCenter Server and creates two clones of the vCenter Server Appliance (Active node).
- vCenter HA network will be configured on the three ESXi nodes to exchange heartbeats and replication information.
- And finally, the vCenter Server Appliance is protected by vCenter HA
Conclusion
vCenter High Availability (VCHA) is a great feature introduced in vSphere 6.5 and it had the ability to provide High Availability for your vCenter Server. Active-passive architecture vCenter High Availability (VCHA) safeguards your vCenter Server appliance from the host, hardware, or application failures. In this article, we have shared the details about vCenter High Available feature and different deployment models and configuration types. Next Article we will share the vCenter HA configuration steps performing in vCenter Server 6.7 with embed platform controller.

