
Raw device mapping (RDM) is an option in the vSphere environment that enables a storage LUN to be directly presented to a virtual machine from the storage array .
Mostly RDM will be used for confiuring clusters ( SQL , Oracle ) between virtual machines or between physical and virtual machines .Also or where SAN-aware applications are running inside a virtual machine. Compare to VMFS , RDM produce similar input/output (I/O) and throughput in random workloads. For sequential workloads there is a small I/O block sizes, RDM provides a slight increase in throughput compared to VMFS. But the performance gap decreases as the I/O block size increases for RDM also for workloads, RDM has slightly better CPU cost .
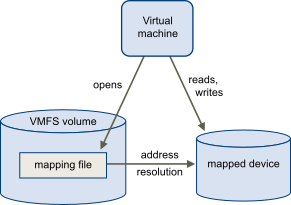
An RDMwill be mapped as a file in a separate VMFS volume that acts as a proxy for a raw physical storage device. Virtual machine can access the RDM directly from storage device . The RDM contains metadata for managing and redirecting disk access to the physical device.The mapped file will give some of the advantages of direct access to a physical device, but keeps some advantages of a virtual disk in VMFS. As a result, it merges the VMFS manageability with the raw device access.
RDM can be used in the following situations
When SAN snapshot or other layered applications run in the virtual machine because RDM enables backup offloading systems by using features inherent to the SAN.
Clustering scenario that spans physical hosts, such as virtual-to-virtual clusters and physical-to-virtual clusters.
Two compatibility modes with RDM
Virtual compatibility mode – RDM acts like a virtual disk file. The RDM can use snapshots.
Physical compatibility mode – RDM offers direct access to the SCSI device for those applications that require lower-level control.
Direct-attached block devices or certain RAID devices will not support RDM. The RDM uses a SCSI serial number to identify the mapped device. Because block devices and some direct-attach RAID devices do not export serial numbers, they cannot be used with RDMs.
Cannot use snapshot feature with RDM in physical compatibility .Physical compatibility mode allows the virtual machine to manage its own, storage-based, snapshot or mirroring operations.
Snapshots feature is available for RDMs with virtual compatibility mode.
You cannot map to a disk partition. RDMs require the mapped device to be a whole LUN.
For vMotion support with RDMs, maintain consistent LUN IDs for RDMs across all participating ESXi hosts.
Flash Read Cache does not support RDMs in physical compatibility. Virtual compatibility RDMs are supported with Flash Read Cache.
RDM cannot be used in every situation. but RDM provides several benefits , find below for understand few of them
User-Friendly Persistent Names
Provides a user-friendly name for a mapped device. When you use an RDM, you do not need to refer to the device by its device name ,you can refer fit by the name of the mapping file .
Dynamic Name Resolution
Stores unique identification information for each mapped device. VMFS associates each RDM with its current SCSI device, regardless of changes in the physical configuration of the server because of adapter hardware changes, path changes, device relocation, and so on.
Distributed File Locking
Makes it possible to use VMFS distributed locking for raw SCSI devices. Distributed locking on an RDM makes it safe to use a shared raw LUN without losing data when two virtual machines on different servers try to access the same LUN.
File Permissions
Makes file permissions possible. The permissions of the mapping file are enforced at file-open time to protect the mapped volume.
File System Operations
Makes it possible to use file system utilities to work with a mapped volume, using the mapping file as a proxy. Most operations that are valid for an ordinary file can be applied to the mapping file and are redirected to operate on the mapped device.
Snapshots
Makes it possible to use virtual machine snapshots on a mapped volume. Snapshots are not available when the RDM is used in physical compatibility mode.
vMotion
vMotion is supported with RDM devices . The mapping file acts as a proxy to allow vCenter Server to migrate the virtual machine by using the same mechanism that exists for migrating virtual disk files.
 SAN Management Agents
SAN Management Agents
you can run some SAN management agents inside a virtual machine. Similarly, any software that needs to access a device by using hardware-specific SCSI commands can be run in a virtual machine. This kind of software is called SCSI target-based software. When you use SAN management agents, select a physical compatibility mode for the RDM.
N-Port ID Virtualization (NPIV)
NPIV technology that allows a single Fibre Channel HBA port to register with the Fibre Channel fabric using several worldwide port names (WWPNs). This ability makes the HBA port appear as multiple virtual ports, each having its own ID and virtual port name. Virtual machines can then claim each of these virtual ports and use them for all RDM traffic.
VMware works with vendors of storage management software to ensure that their software functions correctly in environments that include ESXi. Find below few applications
Such software uses a physical compatibility mode for RDMs so that the software can access SCSI devices directly.
Note:Various management products are best run centrally (not on the ESXi machine), while others run well on the virtual machines. VMware does not certify these applications or provide a compatibility matrix. To find out whether a SAN management application is supported in an ESXi environment, contact the SAN management software provider.