Access Logix
Access Logix is a storage system-based licensed software. This feature lets you enable data access and create storage groups on shared storage systems. This software runs on each storage processor.
Access Logix functionality
- LUN masking – it is an process that makes a LUN available to some hosts and unavailable to other hosts. I describe it a little bit more below.
- Presents a ‘virtual storage system’ – by LUN masking, LUNs are presented only to server(s) which are authorized to see them. In effect, it presents a ‘virtual storage system’ to each host.
- Maps VNX LUNs to host LUNs – mapping VNX LUNs, often called Array Logical Units (ALUs)to host LUNs or Host Logical Units (HLUs). It determines which physical addresses each attached host will use for its LUNs. This feature is configurable by the storage admin.
- Manages Access Control List – access to LUNs is controlled by information stored in Access Logix database, which is resident in a reserved area of VNX disk – the PSM LUN (Persistent Storage Manager).
Access Logix limits
- host may be in 1 storage group per storage system. If you add the same host in another storage group it will be removed from the previous one.
- maximum of 4 storage systems per host
- number of host per storage system – depends on the VNX model
- a storage group is local to 1 storage system
- maximum number of LUNs in a storage group, depenends on a VNX model, eg. VNX5500 – 512
Storage group
Storage group is a collection of one or more LUNs (or metaLUNs) to which you connect one or more servers. In other words think of a Storage group as a container, when you define:
- list of servers that belongs to that container
- list of LUNs that belongs to that container
All servers within one storage group can access all LUNs that are in the same storage group. This is called LUN masking.
LUN masking vs LUN Mapping
Below is a diagram of a storage system attached to two hosts. Each host has a storage group associated with it – storage group A for Server A, and storage group B for Server B. The LUNs used on the storage system are sequential, from 0 through 7, but it’s not always like that, and actually you can set it up differently if you wish. ALU is Array Logical Unit, and HLU is Host Logical Unit. Each LUN on the storage system (ALU) has been mapped to a LUN number as seen by the host (HLU).
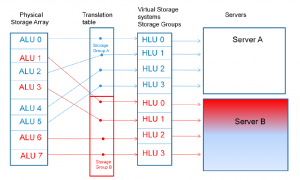
LUN masking vs LUN mapping
The mappings are stored in a translation table, which is part of the Access Logix database. Each server sees the LUNs prezented to it as though they are the only LUNs on the ‘virtual storage system’, represented by the storage group.
Access Control List
While using Fibre Channel, access to the LUNs is controlled by an Access Control List (ACL) which contains the 128-bit Globally Unique ID (UID) of the LUN, and 128-bit Unique IDs of the HBAs in the host. The HBA UID consists of the 64-bit WWNN followed by the 64-bit WWPN.
Each request for LUN access references the ACL, in order to determine whether or not a host should be allowed access.
Registration
Registration is a process of making a host known to the storage system. Connectivity depends on the protocol being used, Fabric logins tell the VNX which ports and HBAs are connected, iSCSI logins tell the VNX which ports and initiators are connected. Registration can be perfomed in a number of ways:
- Automatically, by the Unisphere Agent when it starts
- Manually, through Unisphere or Navisphere CLI
- By using the Unisphere Server Utility

