
Deduplication and compression are the two great space efficiency features on vSAN. With help of these techniques, you will be able to reduce the overall storage consumption on Virtual SAN. As we all know the concept of the duplication since it is been in use from long time by multiple storage and backup vendors, so here I am not going explain more about that but just a brief on that and how vSAN uses this features .
First, you have to understand deduplication and Compression will work with only vSAN cluster with all flash mode ( Cache and Capacity Devices ) . vSAN keep most referenced data blocks in the cache tier while it is active/hot and as soon as the data is no longer active, it is moved to the capacity tier and during this movement vSAN does the deduplication and compression.
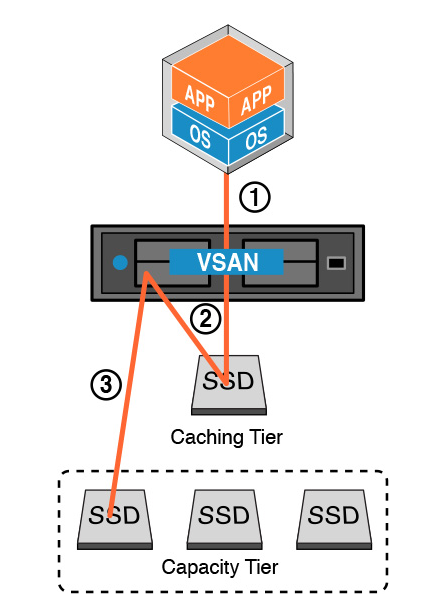
Deduplication and compression processing will occur only the data block is cold (no longer used) and it moved to the capacity tier. Advantage of this process is applications are writing data (same block) or over-written multiple times in the cache tier not on the Capacity Tier and there will not be any overhead on deduplication and compression.
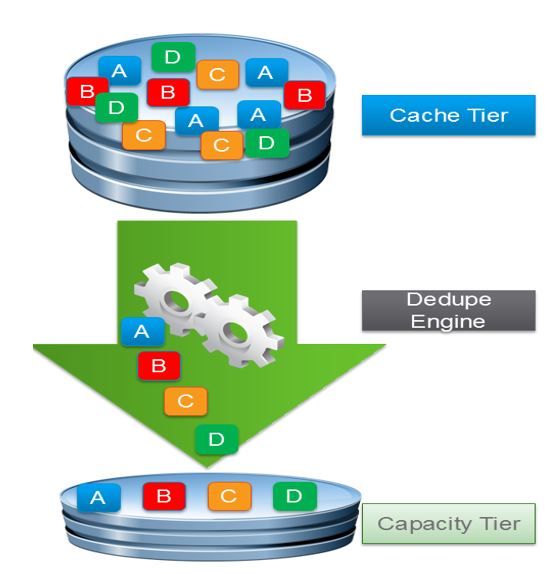
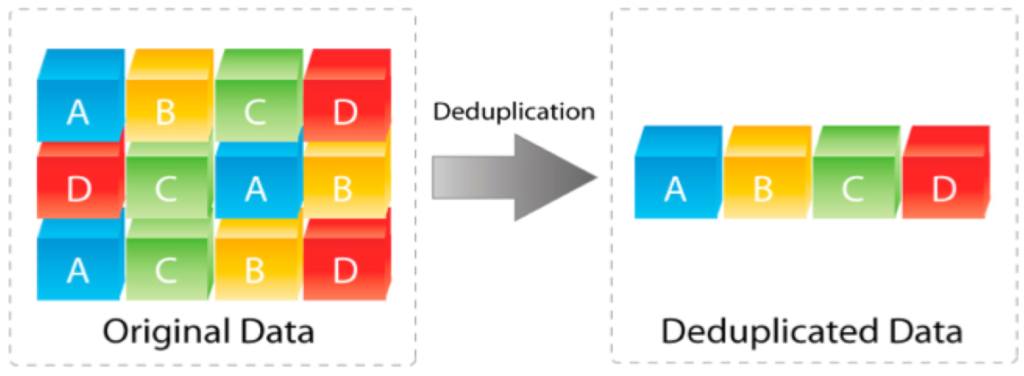
Deduplication
If a block of data is already available on storage, a small reference will create to the existing block instead of writing the whole block again.
VSAN uses the SHA-1 hashing algorithm for deduplication, creates a “fingerprint” for each data block. This algorithm ensure that all data blocks uniquely hashed and multiple same data blocks will not be available on same hash. When a new data block comes in it will hashed and compared to the existing table of hashes. If the data block already available vSAN will add a new reference to it, if the block is not available, a new hash entry will create and the block is persisted.
Compression
This will help to squeeze more blocks to same footprint, VSAN uses the LZ4 compression mechanism and it works on 4KB blocks and get the 4KB block compressed to a size of 2KB.
If a new block found as unique it will go through compression. LZ4 compression mechanism reduce the size of the block to less than or equal to 2KB and compressed version of the block is continued to the capacity tier. If compression cannot reduce the size to less than 2KB, then the full-sized block is remain unchanged.
Deduplication and Compression Points
How Read and Write Operations on Duplication IO Intensity
As I mentioned above deduplication is an IO intensive operation, more operations are performed during the destaging of the data blocks.
Read – While performs a read, extra reads need to be sent to the capacity SSD in order to find the logical addresses and to find the physical capacity (SSD) address .
Write – During destage process, extra writes are required for perform the Hashing the data blocks from cache tier. The hot data on cache tier and hash map tables helps to reduce overheads. Therefore, this overhead has to be accounted, as this is the cause due to the 4KB block is been used.