
ain difference between SnapView Snapshots and VNX Snapshots. VNX Snapshot technology writes the new data to a new area within a pool, without the need to read/write to the old data block. This improves the overall performance compared to SnapView.
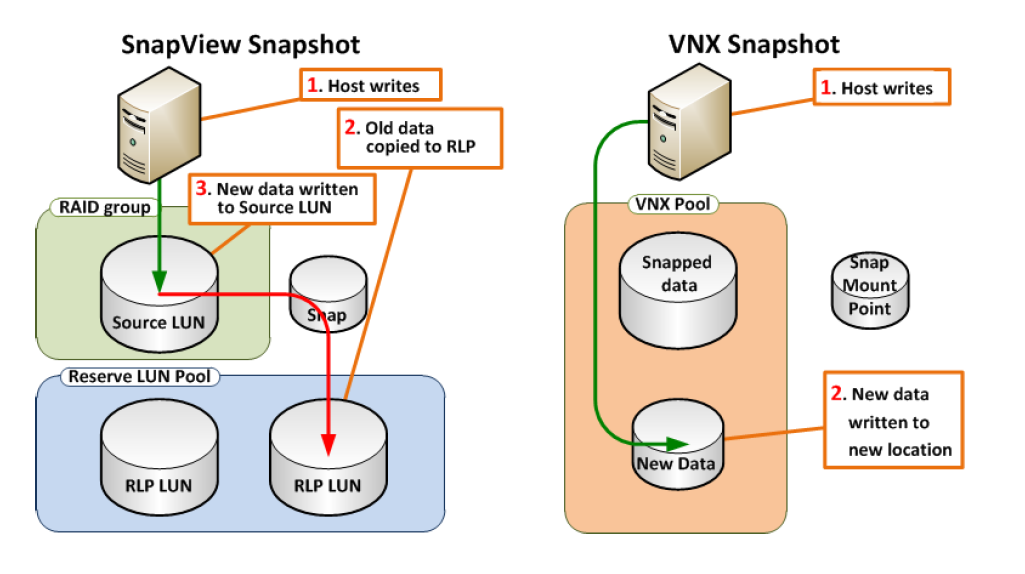
SnapView write vs. VNX Snapshot write
Similarly, during a read from a snapshot, the snapshot’s data is not constructed from two different places as shown below
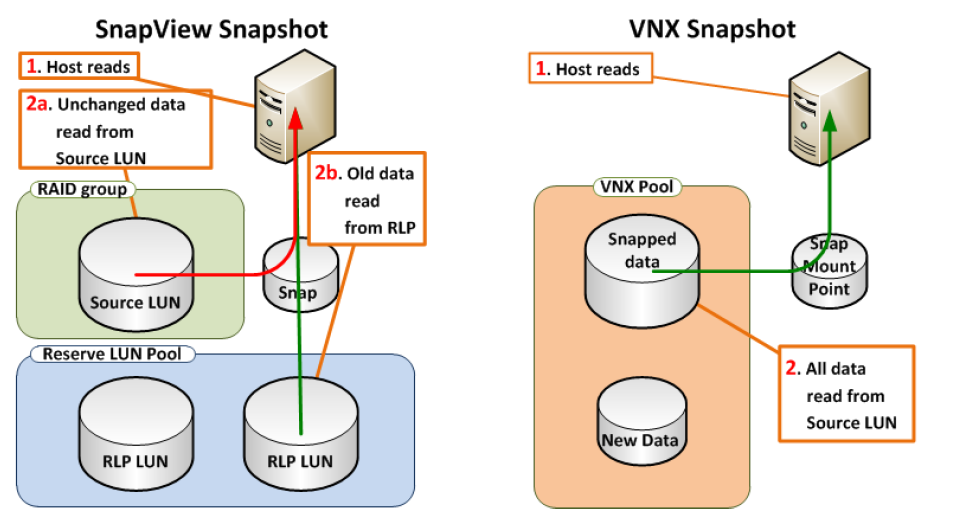
SnapView read vs. VNX Snapshot read
Snapshot granularity
Every VNX Snapshot has 8 KB block granularity. This means that every write occupies at least 8 KB on the pool. The distribution of the 8 KB blocks within a 256 MB slice (1GB in VNX OE for Block R32) is congruent with the normal thin write algorithm.
Check below example , A LUN is snapped with a few blocks of data. The new snapshot points at those blocks, just like the primary LUN.
VNX Snapshot pointing at the same blocks with the LUN at creation time
After a few moments, the primary LUN may receive an I/O that overwrites block A. The first snapshot continues pointing to the original set of blocks A, B, C, and D. After Snap2 is taken, it points to A`, B, C and D.The next primary LUN I/O overwrites block D, and it now points to A`, B,C, and D`.

VNX Snapshots point at unchanged blocks, Primary LUN is using new blocks
When a VNX Snapshot is created on a Thick LUN, portions of its address space are changed to indirect mode. In other words, when writes come in to the Snapped Thick LUN, the LUN starts converting address mapping from direct to 8 KB blocks for each portion of the Thick LUN being written.
Note: Thick LUN remains to be classified as Thick in the CLI and GUI.
The Thick LUN remains in an indirect mode while it has VNX Snapshots.When the last snapshot of the Thick LUN is removed, the mode automatically reverts to direct. The process of reverting to direct mode is not instantaneous, and is performed in the background. The process can be aborted by creating a new VNX Snapshot on the LUN.
VNX Snapshots are a part of the storage pool. A snapshot does not consume space from the pool, until the new data is written to the primary LUN or to the snapshot itself.Snapshot Mount Point Snapshot Mount Point (SMP) is a LUN-like container. It is used to emulate a typical LUN, but provides the ability for the host to write to snapshots and to change snapshots without the need to rescan the SCSI bus on the client.
Snapshot Mount Point (SMP) is a LUN-like container. It is used to emulate a typical LUN, but provides the ability for the host to write to snapshots and to change snapshots without the need to rescan the SCSI bus on the client.

A SMP is created for snapshots of a specific LUN. This means that each SMP can be used only for snapshots of a single primary LUN.To enable access to hosts, SMPs must be provisioned to storage groups just like any typical LUN .