
In my previous post, I have explained how to install the Docker on Cent OS and few important commands can be used for verification and other basic operations. In addition, I have mentioned next topic will be Initial configuration task, which is required.
In this topic, I will be explaining about the initial configuration, which you have to perform after installation of Docker.

The Docker daemon binds to a Unix socket instead of a TCP port. By default that Unix socket is owned by the user root and other users can only access it using sudo. The docker daemon always runs as the root user.
We cannot share root credentials with anyone, so we have to give permission to developers to run Docker. There are two options once
Sudo
The sudo command offers a mechanism for providing trusted users with administrative access to a system without sharing the password of the root user. When users given access via this mechanism precede an administrative command with sudo they are prompted to enter their own password. Once authenticated, and assuming the command is permitted, the administrative command is executed as if run by the root user.
Log in to the system as the root user.
Create a normal user account using the useradd command
# useradd usernameSet a password for the new user using the passwd command
# passwd username

Let try to run docker command with new user we created

Now lets check sudo permission
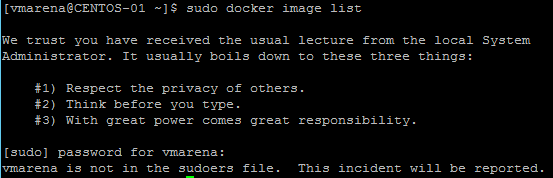
And we confirmed there is no sudo permission for this user , so we have to add the user to sudoers file, you can add this user to the exiting group available on the suodoers or create a new group and configure that in sudoers.
Note:- File sudoers defines the policies applied by the sudo command.
Wheel is a default group available for sudoers, or you can create a new group and add to sudoers file which can be used for setting sudo permission.
# cat /etc/sudoers – Use command to check the contests of the sudoers file
## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands# %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
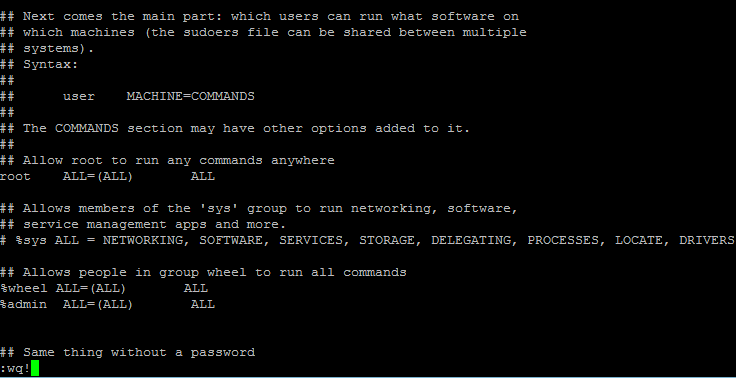
Note:- admin is a group i have created for configure sudo access
If you don’t want to use sudo when you use the docker command, add the users to docker group which will be created while you install and enable docker . When the docker daemon starts, it makes the ownership of the Unix socket read/writable by the docker group.
Add user to Docker Group
usermod -aG docker username

I have added vmarena user to docker group now Log out and log back for the group membership become active .
Verify that you can run docker commands without sudo.
$ docker run hello-world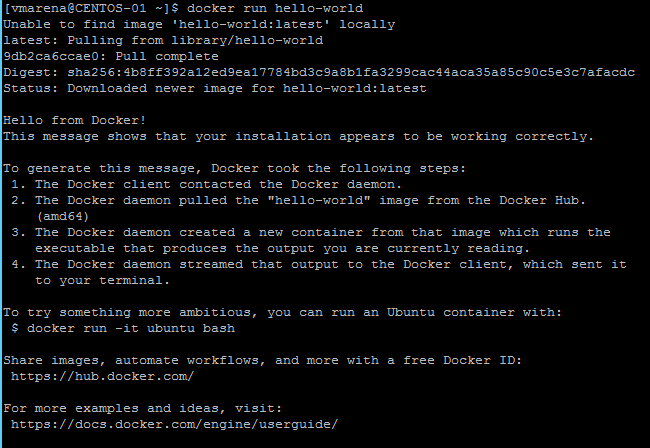
This command downloads a test image and runs it in a container. When the container runs, it prints an informational message and exits.
You can use systemctl to manage which services start when the system boots .
# systemctl enable docker
To disable this use disable instead of enable
# sudo systemctl disable docker
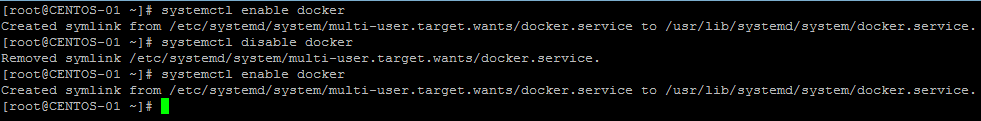
Note:- User configured with docker group will not have the permission to perfomr this , sudo permission required or need use root account .
You will have multiple option to check the docker service status , find below
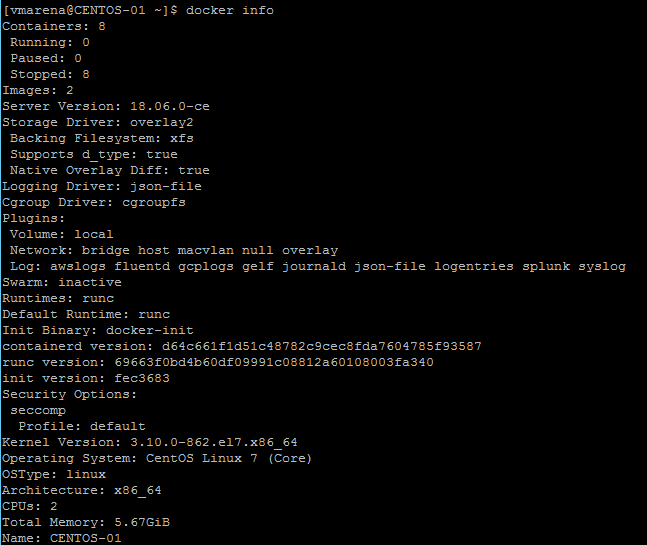
Use the docker info command using to display system-wide information such as status , available containers , images , OS , resources etc
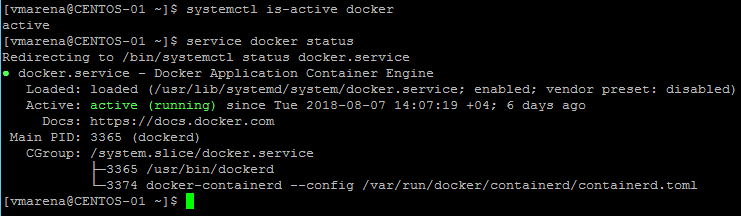
You can also use operating system utilitie systemctl is-active docker or service docker status
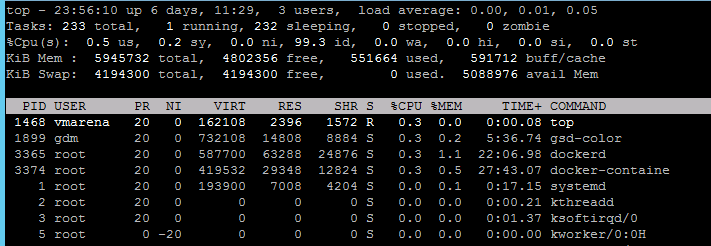
Finally, you can check in the process list for the dockerd process, using commands like ps or top
 First two Lessons are only to start docker and upcoming posts will help you understand how containers works in docker
and you can follow the exercise , Stay Tuned
First two Lessons are only to start docker and upcoming posts will help you understand how containers works in docker
and you can follow the exercise , Stay Tuned
Suggested Posts
Docker Architecture and Components
How Container Differ from Physical and Virtual Infrastructure