
This Post cover below , and mainly for installing and configure VCSA we should have proper FQDN
The first step is to come up with hostnames and corresponding IP addresses for the PSC and vCSA, something like this:
psc65-a.vsphere65.local –> 192.168.16.50
vcsa65-a.vsphere65.local –> 192.168.16.51
Using a DNS server running on a Windows box within my test lab, I went ahead and created a new DNS zone called vsphere65.local. In addition to this, I also created the above listed Forward Lookup (A) records. The Reverse (PTR) records are created automatically if the corresponding tick-box is left checked.
The DNS setup process is captured in the next video.
Both the PSC and vCSA can be deployed using any of two methods; a command line based installer or a GUI driven one. Since simple is generally better, I’ve opted for the GUI installer. The steps are as follows:
Step 1: Download the latest vCSA 6.5 ISO from my.vmware.com.
Step 2: Mount the ISO on the Windows box from where the installation is carried out.
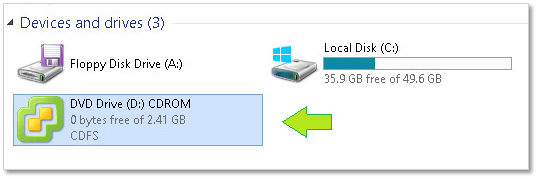
Install vCSA 6.5: Mounting the ISO installer in Windows
Step 3: After the ISO is mounted, drill down to the vcsa-ui-installer\win32 folder and run installer.exe.
Important: Make sure that the Windows box from where the installation is carried out is able to resolve the DNS records previously created (see Prepping DNS).
Select the Install option from the installer’s opening screen. It’s then just a matter of following the installation wizard as shown in the upcoming video.
For all other management operations, such as adding identity sources, users and groups and so on, use https://psc65-a.vsphere65.local/psc/.
Note: URLs will obviously differ in accordance to the DNS names chosen for the appliance and PSC.
With the PSC out of the way, we can go ahead and install vCSA. Yet again, the install is a two-stage affair as per the next and final video. The same checks and installation procedure apply. During the second stage, you have to specify the details entered for the PSC. This is required since we’ve opted for an external PSC rather than an embedded one.
After the installation completes, the vCSA can be managed using the vSphere Web Client or the HTML5 client which, as mentioned many a time, is still a works in progress. Also remember, that the thick (C#) vSphere client can no longer be used to connect to vCenter Server.